AgileDialogs Design Guide
Home –> AgileDialogs Design Guide
Introduction
This document describes the usage of AgileDialogs from dialog-designer perspective.
With AgileDialogs, a designer can create dialogs or scripts to gather information from users and save this information either in Microsoft Dynamics 365 or other systems.
The terms ‘AgileDialog’ and ‘dialog’ are used interchangeably in the rest of the document. To avoid confusion, Dynamics’ own dialogs, are referred to as such, in italic.
AgileDialogs Basics
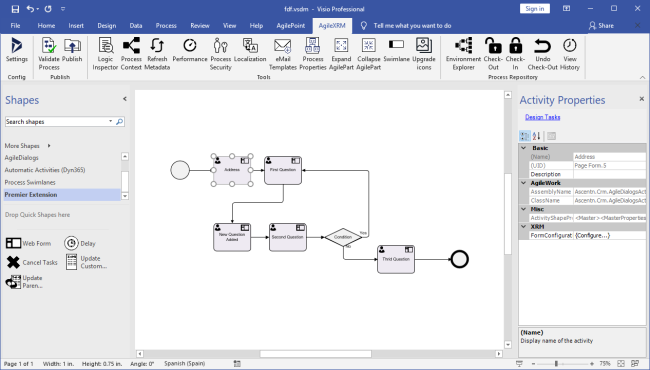
An AgileDialog is a visually designed model comprising of a set of UI steps (Page Forms) and optionally, automatic system steps. The interface presents data and questions to an end-user to inform or get input from the end-user. The flow is modeled using MS Visio.
AgileDialogs can be used for many purposes, for example:
- Self-help guides
- Troubleshooting wizards
- Call Scripts in Call Centers
- Help users fill out complex forms
- Create Surveys
- Create Tests & Exams
AgileDialogs can be executed standalone, meaning the dialog is not part of an AgileXRM process, or they could be part of a business process, that is, the execution of the dialog is a task assigned to an end-user.
From the end-user’s perspective, a dialog is a set of questions that he/she must answer in order to perform a task. Within the dialog, the user can go forward or backward in order to fulfill the required task. The dialog is presented to the end-user using an HTML5-based Dialog Render Engine.
AgileDialogs Design Concepts
These are the basic concepts that an AgileDialog designer must know.
Dialog Model
An AgileDialog Model is a business process drawn and configured in Envision (MS Visio), used for “holding a conversation” with an end-user. This process is different from other AgileXRM processes, as all the tasks are executed synchronously by the end-user; there are no task assignments or tasks lists involved.
AgileDialogs can contain manual tasks (form Pages), decision points (based on context data) and automatic activities (to interact with XRM repository or other systems).
Question
This is the basic unit of a dialog. Each question corresponds to a control (e.g. Textbox, List box, Radio Button, etc.) that is presented at runtime to show to or get information from the user. Each question has a caption, where the designer can specify the content of the question. Beside this caption, the designer can optionally add a tooltip and further help. The content of the controls can be static or dynamic. For example, there is a control that presents a grid using a query to retrieve data from the XRM repository.
Page
Dialog questions are grouped in Pages (a Page is a form with a set of controls). Each Page is a step in an AgileDialog model as defined in Envision. Between Pages, the modeler can include decisions and automatic activities to control the flow and interact with the XRM repository or other systems.
SubDialog
This is for calling an AgileDialog from another AgileDialog. It helps organize complex dialogs into manageable pieces, as well as for creating reusable SubDialogs that can be reutilized in different dialogs. A SubDialog can be called at any point in the parent dialog (not just as the last step) and the Back-Next functionality works as expected between dialogs and SubDialogs.
Validation
AgileDialogs provides validation features.
All controls have a Required property, when this is TRUE, the user must fill the control to continue with the dialog.
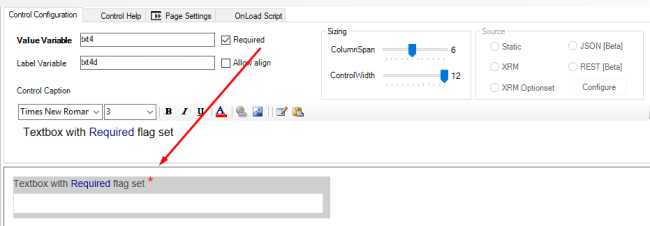
The Validation error message is customizable via the ValidationMessage property.
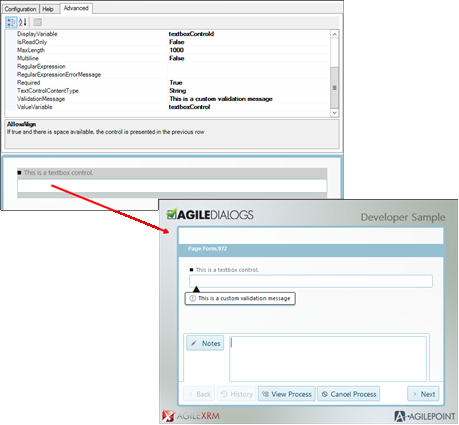
In the case of Text controls, there is specific validations to check max length for strings, validate using regular expressions or type (validate that a string is an integer, decimal). Additionally, the designer can include JavaScript code to perform more complex validations.
We also have the CustomValidationMessage property available for input controls that allows us to configure and locate a message for custom validations.
Context
The dialog has access to a context. These are dynamic values which are used in the dialog.
The context available depends on these criteria:
| Context available in dialog | |
|---|---|
| No Main Entity set (Recommended for performance reasons) | Preset Process Variables |
| Main Entity Set (Not recommended for AgileDialogs) | Preset Process Variables |
- Responses from Questions
- Responses from Questions
- Main Entity Schema
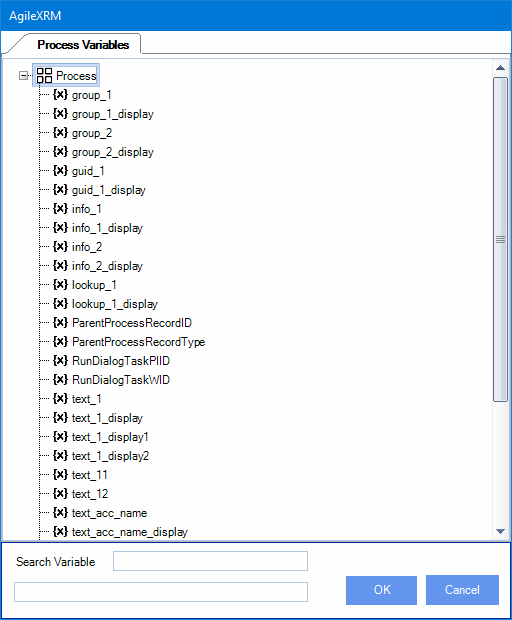
The following 4 Preset Process Variables are only usable if the AgileDialog is executed as a Task in an AgileXRM Process, and help to interact with the parent process and the entity record it is managing:
-
ParentProcessRecordID: ID of the main entity in the parent process that contains the task. This ID can be used to work with the record in the dialog (e.g. Update its status)
-
ParentProcessRecordType: Type of the main entity in the parent process (e.g. account)
-
RunDialogTaskPIID: Process instance ID of the process that contains the task that corresponds to the execution of the Dialog. This can be used, for example, to update a variable in the context of the parent process from within the dialog.
-
RunDialogTaskWID: ID of the Workitem that corresponds to the execution of the Dialog. This is for information purpose only and has no other use.
Besides these variables, there are generic purpose variables (image below):
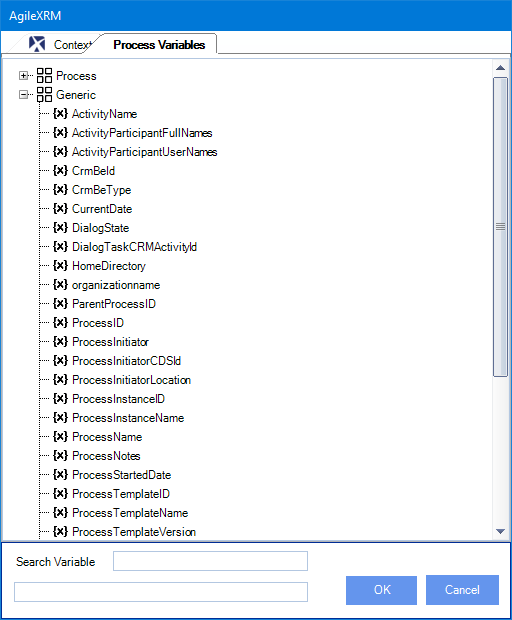
The most important ones are described in depth here:
-
CrmBeId: This is the record id of the main entity.
-
CrmBeType: This is the type of the process main entity, for example account or incident.
-
organizationname: This is the name of the CRM organization that the process record belongs to.
-
DialogTaskCRMActivityId: If part of Dialog Activity, this property holds the CRM Activity ID that launched the current dialog instance.
This document lists all available variables under the Generic node
Render Modes
AgileDialogs Pages can be configured to be shown in three different types of views, from a User Experience point of view. When Designing an AgileDialogs Process Template, it is possible to manipulate the way that every Page Form is shown on Screen, for decorative / functional purposes. It is also possible to combine different types of visualization in a Process, as each Page Form has its own visualization setting.
To Change the visualization style for the Page, perform the following steps (Pictures below):
Figure 1. Access to the Page Form and click “Options”
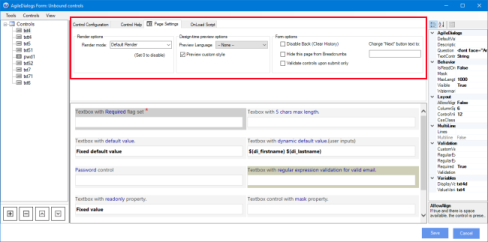
Figure 2. Once we are inside the Page Form designer, we click on “Options”
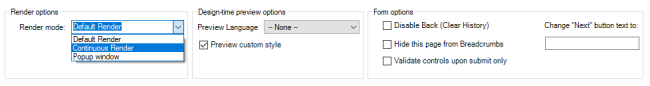
Figure 3. Once there, you can choose your preferred render mode for the current Page
The three view modes to be described are:
-
Default Render. Every time we access to the next Dialog Page, we remove the previous page. Set by default when creating a new Dialog Page.
-
Continuous Render. When moving forward through our process instance, the previous pages of the dialog remain on screen, and if we click on any of them, we would go back to that page.
-
Popup Mode. The page form marked with this Render mode, will be shown as a popup over the current page.
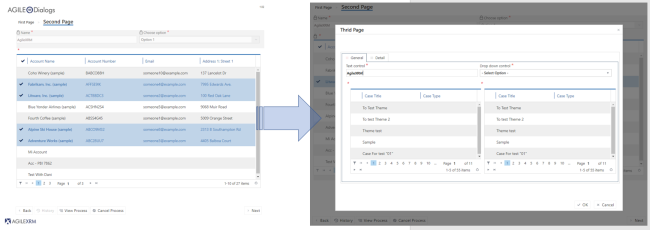
Figure 5. Page Form shown on “Popup Mode”
AgileDialogs Design
There is a specific Visio template to create AgileDialogs:

When this template is selected a new AgileDialog is created. The first thing to do is to configure the interaction between the dialog and CRM in XRM Connection window.
XRM Connection Window
Check XRM Connection Window documentation in this link: XRM Connection Window
AgileDialogs Security
Check AgileDialogs Security documentation in this link: AgileDialogs Security
AgileDialogs Shapes
In Envision, these stencils contain the shapes specific to AgileDialogs:
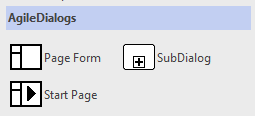
There are 5 shapes in total, four in the XRM AgileDialogs stencil and one in the XRM External Connector stencil:
-
Page Form: is a step in an AgileDialog where the form is configured. The form can contain multiple controls of various types
-
Start Page: is a step in an AgileDialog where the form is configured, but it does not creates an AgilePoint process until its completed. The form can contain multiple controls of various types
-
SubDialog shape: allows calling another AgileDialog where this step is used. There are two important differences with CRM’s own sub-dialog functionality:
-
A SubDialog step can be used anywhere in an AgileDialog, and not just as the last step
-
The Back button works correctly no matter how complex the hierarchy. In CRM dialogs, it is not possible go back to the parent dialog; limiting the end-user experience.
-
-
Dialog Task: is used in an AgileXRM Process (and not in an AgileDialog model) as a Task for a Full User. Upon opening the task in CRM, the user is presented with the associated AgileDialog.
-
Intranet Dialog Task: is used in an AgileXRM Process as a Task for a Process Participant User. Upon opening the task in the Portal, the user is presented with the associated AgileDialog. The Task is Completed when the user completes the dialog.
-
Internet Dialog Task: used in an AgileXRM Process (and not in an AgileDialog model) as a Task for an External User. Upon opening the task in the Portal, the user is presented with the associated AgileDialog. The Task is Completed when the user completes the dialog.
Apart from these, most shapes in the AgileXRM Automatic Activities stencil can be used in dialog models. The following shapes cannot be used in an AgileDialog model:
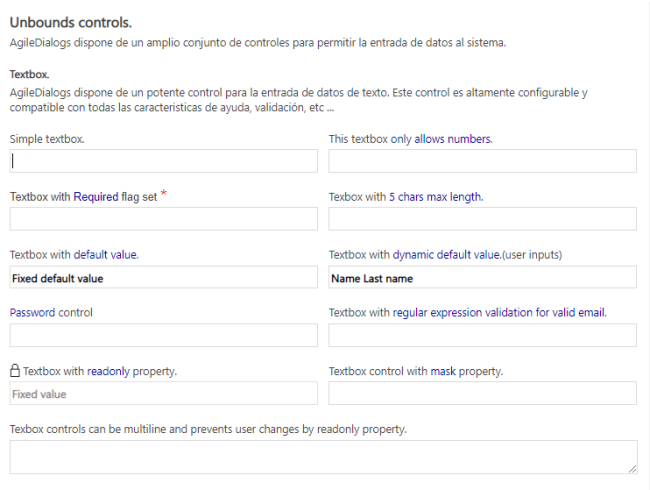
Control Types
Currently the following control types are available, and each type has specific configuration besides the common properties.
- Calendar
- Checkbox
- Combo
- Currency Control
- File
- Grid
- Group Container
- HTML
- IFrame
- Info
- Lookup
- Numeric
- Password
- Radio
- Search
- Tab Container
- Textbox
- Variable Control
- Widget Control
- Yes/No
Advanced Features
Breadcrumbs
AgileDialogs Rules editor
AgileDialogs Progress Messages
AgileDialogs Progress Messages
User Feedback
Localization
Performance Window
JavaScript Extensions
Hosting dialogs inside a Portal
Hosting dialogs inside a Portal
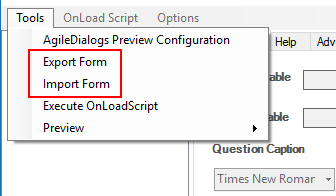
Exporting and Importing Page configuration
The form definition can be exported to an XML file or imported from an XML file using the menu options available in Tools menu:
Launching a Dialog using a URL
AgileDialogs can be launched using a URL, there is no need to have an associated XRM record nor an AgileXRM task.
An AgileDialog can be used, for instance, to create a record in XRM helping the user to fill the data avoiding the use of complex forms or to get data to call other system using a web service.
The format of the URL to launch a dialog is:
http://<SERVER_URL>/AgileDialogs/AgileDialogsKendoRuntime.aspx?orgname=<ORGANIZATION_NAME>&DefaultProcessTemplate=<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>
This URL can be used in portals to allow the users starting dialogs on demand.
In order to make this work, the user must have permission to start instances of the dialog template.
Language Setting
When the dialog is localized and the link must open a specific language, the URL can contain the Locale ID of the language, the format of the URL in this case is:
http://<SERVER_URL>/AgileDialogs/AgileDialogsKendoRuntime.aspx?orgname=<ORGANIZATION_NAME>&DefaultProcessTemplate=<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>&lcid=<USER_LOCALE_ID>
For a list of Locale IDs see:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/0h88fahh(v=vs.85).aspx.
The value to pass is in the column Decimal Value, for instance for 3082 for Spanish or 1036 for French.
Action after dialog finishes
When creating a link to open a dialog it is also possible to specify what to do when the dialog is finished. There are several options based on the use of the URL query string parameter AfterSubmit*:
- Close the window when dialog finishes. This is useful when opening the dialog in a new window
http://<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>/AgileDialogs/AgileDialogsKendoRuntime.aspx?orgname=<ORGANIZATION_NAME>&DefaultProcessTemplate=<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>&AfterSubmit=Close
- Redirect to another URL. This approach is used to return to the calling page instead of closing the window
http://<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>/AgileDialogs/AgileDialogsKendoRuntime.aspx?orgname=<ORGANIZATION_NAME>&DefaultProcessTemplate=<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>&AfterSubmit=<URL_TO_REDIRECT_TO>
- It is also possible to handle where a Dialog should be redirected to, once it is completed with the “Template AfterSubmit” parameter. This parameter can be found in Envision, inside AgileDialogs settings, in the “Options” tab (see image below).
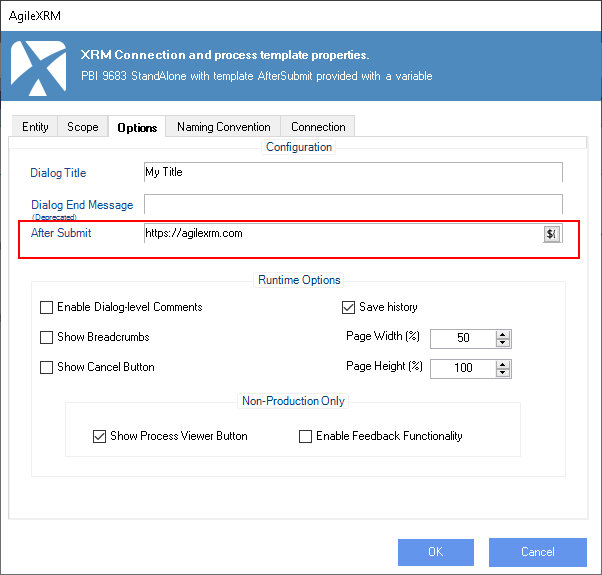
This field supports the use of any AgileXRM context variable. Furthermore, it is also possible to use a special parametrization which allows to redirect to anywhere inside the current Dataverse/D365 Organization. This parametrization is based on the “Xrm.Navigation.navigateTo()” function from Client PowerApps API (see full details in this URL: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/power-apps/developer/model-driven-apps/clientapi/reference/xrm-navigation/navigateto)
So, in addition to any valid URL, similar expressions to the following are fully supported for any dialog executed in hosted mode in Dynamics365/Dataverse environment:
- Record Navigation
API Notation
pageType=entityrecord&entityName=account&entityId=${guid_account}Native URL Notation
pagetype=entityrecord&etn=account&id=${guid_account} - View Navigation
API Notation
pageType=entitylist&entityName=account&viewId=<myviewId>&viewType=savedqueryNative URL Notation
pagetype=entitylist&etn=account&viewid=<myViewId>&viewType=1039 - Dashboard Navigation
API Notation
pageType=dashboard&dashboardId=<myDashId>&type=systemNative URL Notation
pagetype=dashboard&id=<myDashId>&type=system - WebResource Navigation
API Notation
pageType=webresource&webresourceName=new_MyPageNative URL Notation
pagetype=webresource&webresourceName=new_MyPage
IMPORTANT NOTE: “URL AfterSubnit” overiddes “Template AfterSubmit” parameter, if the latter is configured.
Enable/Disable automatic control focus
By default, AgileDialogs focuses the first control on the page. This behaviour is usefull for the most cases, but sometimes we want to render AgileDialogs but prevent this behaviour. We can control this using autofocus parameter.
Available values for autofocus parameter are:
- 0 Use this value to disable autofocus behaviour
- 1 USe this value to enable autofocus behaviour. This is the default value, so this case can be ignored.
http://<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>/AgileDialogs/AgileDialogsKendoRuntime.aspx?orgname=<ORGANIZATION_NAME>&DefaultProcessTemplate=<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>&autofocus=<[0|1]>
Creating links to complete a Dialog Task
Sometimes the process modeler needs to send an email to a user with a link to complete a task that consists of a dialog. The email needs to be sent using the Notification mechanism of the Dialog Task shape so that the WorkItem ID can be sent.
The format of this URL is:
http://<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>/AgileDialogs/AgileDialogsKendoRuntime.aspx?orgname=<ORGANIZATION_NAME>&DefaultProcessTemplate=<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>&wid=<AGILEXRM_WORKITEM_ID>
When the user opens this URL the dialog is either started (the first time that the user opens this URL) or resumed if the user is returning to this dialog.
Accessibility
Enable/Disable Section 508 mode
AgileDialogs has a mode that will render the UI compatible with the US Government’s Section 508 requirements.
To enable this mode, the URL to initiate the dialog should contain the s508 parameter set to 1:
http://<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>/AgileDialogs/AgileDialogsKendoRuntime.aspx?orgname=<ORGANIZATION_NAME>&DefaultProcessTemplate=<PROCESS_TEMPLATE_NAME>&s508=1
Cancelling a dialog
There are various ways that a dialog may be cancelled:
By User
AgileDialogs that are associated to a task (Dialog Task, Intranet Dialog Task and Internet Dialog Task) can be cancelled by the user if the modeler allows it by setting the Enable Cancelation parameter to true:
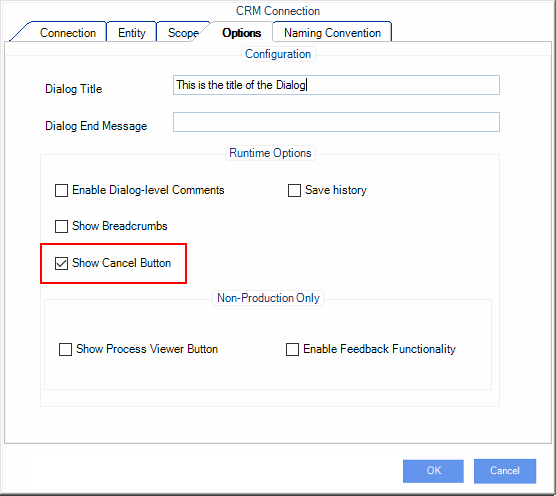
When the dialog is canceled the corresponding task in the parent process is canceled and the process continues.
By System
Dialogs will also be automatically canceled when the Expected Time property which is set at the dialog level is surpassed.
While the dialog is not canceled the user can suspend and open it in the last page whenever he wants.
Dialogs that are run on demand (that is, they are not associated with a task) are automatically canceled when Expected Time parameter of the dialog is exceeded: